New cybercrime on the rise, warn experts simranOctober 30, 2025
simranOctober 30, 2025
New cybercrime on the rise, warn experts
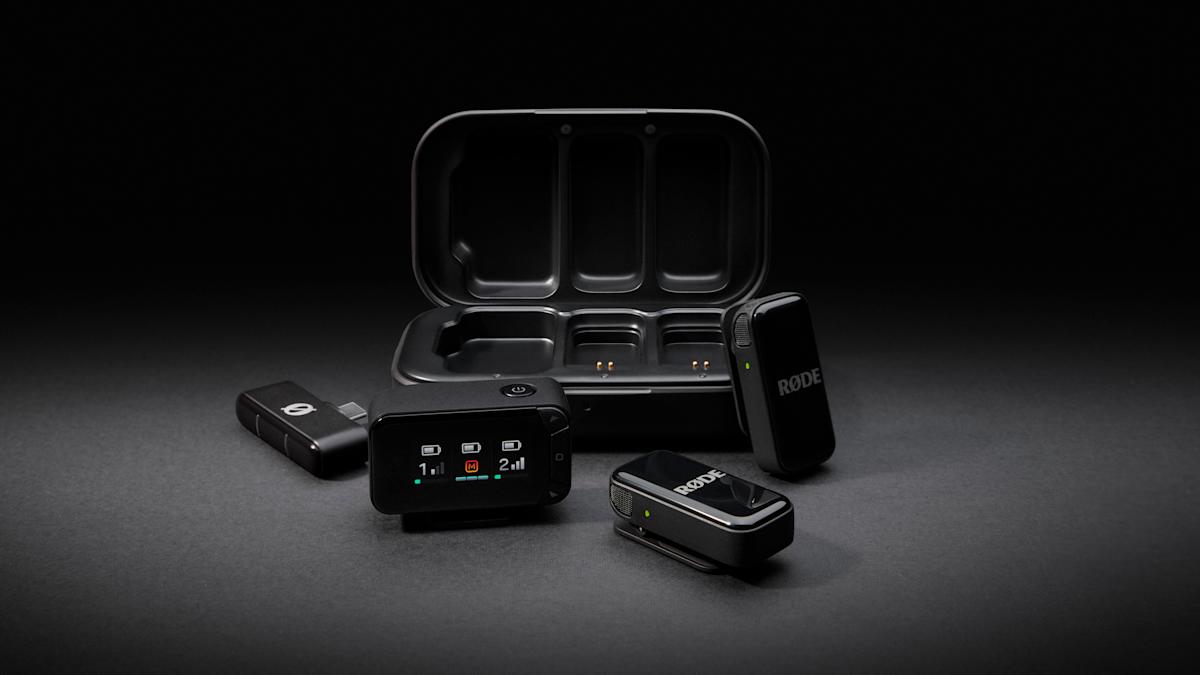

Rode’s wireless mics now work with digital camerasNews mrsk_sumitOctober 30, 2025
mrsk_sumitOctober 30, 2025
Rode’s wireless mics now work with digital cameras

Jennifer Schumacher on Agency MistakesWordpress simranOctober 30, 2025
simranOctober 30, 2025
Jennifer Schumacher on Agency Mistakes

IntrCity SmartBus raises $30M at $140M valuationNews mrsk_sumitOctober 30, 2025
mrsk_sumitOctober 30, 2025
IntrCity SmartBus raises $30M at $140M valuation

Beware of fake challan apks: Cops simranOctober 30, 2025
simranOctober 30, 2025
Beware of fake challan apks: Cops